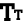Achievements
Efficacy of indigenous strains of probiotics for human health
A collection of proven indigenous strains of probiotic lactobacilli isolated from faecal samples from healthy human subjects and other sources was established at NDRI, Karnal under a DBT funded network collaborative project to harness their general and specific health benefits most optimally in the target population. Molecular techniques such as PCR, sequencing of 16S rRNA and housekeeping genes (rpoA, pheS and tuf), RAPD and MLST were developed for the identification of probiotics at genus, species and strain level. MLST (Multi Locus Sequence Typing) Scheme was developed using eight housekeeping genes (pgm, ddl, gyrB, purK1, gdh, mutS, tkt4 and phe) for indigenous probiotic isolates of Lactobacillus plantarum, and established Eleven “Sequence Types”(ST) for Lactobacillus plantarum.
Whole genome sequence of indigenous L. plantarum Lp91, L. fermentum Lf1 and Lbs2
The draft genome sequences of Indigenous probiotic strains MTCC 5690 (Lactobacillus. plantarum Lp91) and MTCC 5689 (Lactobacillus fermentum Lf1) and Lbs2 have been determined.
Deposition of proven probiotic Lactobacillus strains at MTCC under Budapest Treaty for safe deposit and as per ICMR-DBT guidelines
5954. plantarum Lp91, L. fermentum Lf, Lactobacillus casei Lbs2 and Lactobacillus fermentum Lbs4 have been deposited at International repository at MTCC under Budapest Treaty for safe deposit and as per ICMR-DBT guidelines wherein there is a requirement that any probiotic lactobacillus to be commercialized should be deposited in an International repository. The strains names are Lp91 as MTCC 5689, Lf1 as 5690, Lbs2 as MTCC 5953 and Lbs4 as MTCC 5954.
Probiotic attributes and functionality
The probiotic Lactobacillus strains exhibited all the desirable probiotic attributes under simulated gut conditions and exhibited anti-inflammatory potential both in vitro as well as in animal models
plantarum Lp91 expressed hypocholesterolaemic effects in rat model. Lp91 and Lf1 improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in C57BL/6J male mice fed on high fat diet (HFD) for a period of six months and prevented the development of diabetes.
Two of our potential probiotic strains viz. Lp91 and Lf1 could effectively ameliorate both 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced colitis in mouse models respectively. The possible mechanism of anti-colitic action by Lp91 included down regulation of inflammatory biomarkers and up regulation of IL-10 by Lp91. L. fermentum Lf1 on the other hand exhibited a protective role in oxidative stress induced colitis.
Gut hormone secretion could be observed using in vitro cell line model of endoenterocrine cells (NCI H716 and STC-1).
The technology of lab scale production of three most popular traditional fermented dairy products viz. dahi, lassi and shrikhand supplemented with Lp91 has been developed.
Cell wall components
It has been recognized that cell wall components as the Microbe Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs) not only could help in probiotic adhesion but also elicit specific immune response by interacting with Pattern Recognition Receptors and can act as immunobiotics. Hence, cell wall components like surface proteins, peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid have been isolated from probiotics strains and investigated for their anti-inflammatory potential in DSS colitis mouse model. This can pave way for exploring these purified cell surface components for developing into novel pharmabiotics for boosting immunity in immuno-compromised individuals with low tolerance to heavy dose of live cells of probiotic strains.
Anti-inflammatory effect of surface proteins and peptidoglycan of probiotic lactobacilli in colitis mouse model demonstrated that surface proteins may offer a safer preventive and therapeutic option for combating inflammatory disorders
Heat killed cells of probiotic lactobacilli were also found to reduce the inflammatory response through down regulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α secretion both in in vitro cell line and in vivo colitis mouse model.
Diet and Gut Microbiota
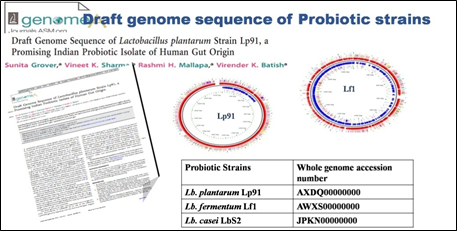
Realizing the tremendous importance of the role of indigenous probiotics in human health from Indian perspective, a joint collaborative project on “Comparative metagenome of human gut of North and North-eastern region of India” with financial support from DBT was taken up to study the gut microbiota in north and north east Indian population representing totally different dietary situations with different food habits.
North-Eastern human Gut microbial diversity was studied between vegetarian and non-vegetarian population under different age groups (20-30 and 50-60). No significant gut microbial changes were observed at the phylum and Family level in all the population groups except Enterobacteriaceae and Veillonellaecae which showed higher abundance in the gut microbiota of North-Eastern population compared to North India
Gut microbiota composition was found to be distinctive in Autistic children. Among the four predominant phyla, decreased abundance of Firmicutes phylum and increased abundance of Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria was observed in ASD children.
The comparative analysis of predominating Gut Enterotypes in children of varying nutritional status (malnourished children) showed significant (P<0.05) decrease in the abundance of Bifidobacteria with the decline in the nutritional health of the children using abosolute qPCR quantification approach. Metagenomic and metabolomic profiles of indigenous dairy cattle and fermented milk products
Work has been initiated to investigate the metagenomic and metabolomic profiles of indigenous dairy cattle under different dietary regimens and to uneveil the metataxonomics of dahi- an Indian traditional fermented product used in different parts of country
Anaerobic Microbial Fermentation
The anaerobic microbiology lab has been working on the diversity of obligately anaerobic rumen fungi, development of biomarkers for improving their taxonomy, mitigation of enteric methane using various approaches and administration of direct-fed microbials for improving the animal productivity. Besides, our research group also explored the role of probiotics, especially through digestive enzyme(s) inhibition and conjugated linoleic/ linolenic acid production.
- In our research group, we have reported two novel genera of anaerobic fungi (Oontomyces anksri & Buwchfawromyces eastonii), which were only the 7th & 8th genera since their discovery in mid-seventies.
- Developed a method for differentiation of genera/ species of these fungi using D1/D2 domain of large-subunit r-DNA. Our research group also developed the formulation of most-efficient direct-fed microbials that improved animal nutrition & productivity.
- Contributed towards understanding the diversity of methanogens and methane-mitigation interventions. Our research group also isolated health-promoting probiotics that produces conjugated linoleic/ linolenic acids, transform isoflavones or control postprandial hyperglycemia.
- Our research group also developed technologies like ‘methods for long-term preservation of anaerobic fungi’; ‘micro-encapsulation of probiotics’; ‘method for detection of antibiotics in milk’; and ‘SSF-ENLAC technology’.
Neocallimastix sp.

Anaerobic fungi growing on rice straw
Anaeromyces sp.
Techno-Functional Starters Lab (TFSL)
Scheme on Dairy Microbes under Network Mode-VTCC
A total of 655 lactic cultures have been isolated from dairy and non-dairy samples and after identification were deposited in VTCC culture bank. These cultures have been evaluated for technological and functional properties. Pediococcus cultures with galactose utilization, phytase activity, EPS producing, probiotic and antimicrobial activity have been characterized.
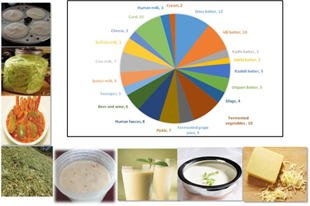
More than 100 lactic cultures from cold dessert region have been isolated and characterized. Lactococcus lactis cultures used for preparation of Dahi and Gouda cheese showed overall better acceptability in terms of less bitterness, more flavour production, better compatibility and characteristic eye formation.

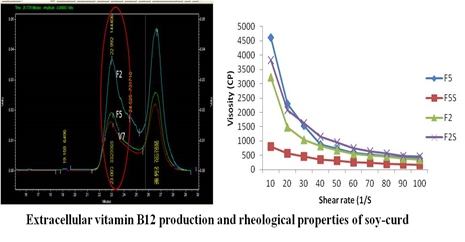
Production of extracellular Vitamin B12 by lactobacilli and ameliorative effect of vitamin B12 bioenriched soy based functional food on adverse pregnancy outcomes of Wistar rat
Vitamin B12 producing lactobacilli (L. plantarum F2, V7, F9, and L. rhamnosus F5) have been isolated from infant’s fecal sample. Lactobacillus plantarum F2 endowed with highest extracellular vitamin B12 production Developed vitamin B12 bio-fortified soy-curd with Lactobacillus plantarum F2 contains appreciably higher vitamin B12 than other soy-fermented foods. Vitamin B12 produced by Lactobacillus plantarum F2 was bioavailable and ameliorate the adverse pregnancy outcomes in wistar rats
Bioprocess for bioactive peptides from whey
Bio-process for bioactive peptides production from whey was developed for formulation of functional food. Bioactive peptides (3-1 kDa fractions) have shown highest ACE and alpha-glucosides inhibitory activity in vitro.
Proteome analysis of Lactobacillus strains in response to stresses
Acid and bile responsive differential proteome changes in L. fermentum strain at pH 2.5 have been investigated by LFQ technique. Bile responsive proteome changes in L. fermentum NCDC 400 and L. helveticus MTCC 5463 have been investigated by high throughput mass spectrometry techniques. Proteins involved in protein and carbohydrate metabolisms were highly up-regulated in Lactobacillus strains. Genome analysis of NCDC 400 revealed large number of hydrolase family genes which might assist this strain to overcome deleterious effect of bile.
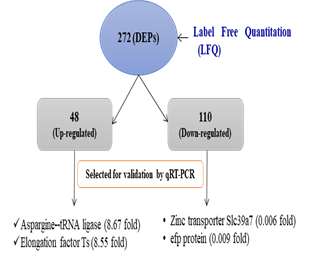
Acid responsive DEPs in NCDC 400

Differential Expression Analysis (Control Vs 1.2%) bile treated
Draft genome of NCDC400
Cholesterol Binding Exopolysaccharides from Lactic Acid Bacteria
Cholesterol binding exopolysaccharides “EPS 400” from Lactobacillus fermentum NCDC 400 has been characterized. EPS400 @ 2% showed maximal binding of cholesterol (90.32±0.2%) in vitro without affecting stability at low pH. Feeding of EPS 400 to Hypocholesterolemic rats showed about 16.5% total cholesterol reduction in serum, 17.41% in liver and 12.17% adipose tissue. EPS 400 exerted significant hypocholesterolemic effect on rats fed with cholesterol diet.

Bioactive peptides
Among all the species, sheep milk derived peptides in 10kDa fraction showed maximum antimicrobial activity followed by cow and buffalo milk. Higher antioxidant and antihypertensive activity were seen in sheep milk peptides in 5kDa fraction followed by cow and buffalo milk.
ACE inhibitory peptides sequence identified in fermented milk-derived peptides are VRGPFPIIV, IPYVRYL (ovine), AVPYPQR, (camel), FLPYPY., KAVPYPQR, LPYPY PQKAVPYPQ (caprine). Peptides with Antioxidant activity is AVPYPQR (Ovine), SRYPSYGIN (camel) and PQQVSALPPPPMQY (caprine). Potent antimicrobial peptides QPKTKVIPYVRYL, YQEPVLGPVRGPFPII, IPIQYVL, LYQEPVLGPVRGPFPII (ovine) PVVVPPFLQPE, (caprine) and immuno-modulatory activity YQEPVLG (ovine, caprine and camel).

HPLC chromatogram of A. Goat milk B.Sheep milk derived peptides
plantarum C2 fermented soya milk derived bioactive peptides had antimicrobial, ACE-Inhibitory and anti-oxidative properties in 10 kDa peptide fractions.
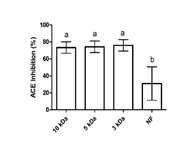
Functional fermented foods
The fermented productPanchamritwas optimized by using Dahi and milk (2:1) and addition of honey, sugar and ghee and was stable for 4 weeks. Panchamrit had antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activity as observed in HT-29 cell line and was stable for 4 weeks.
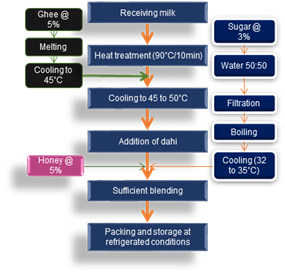
Flow Chart for preparation of Panchamrit
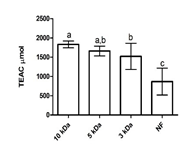
NCDC 144 yoghurt culture was used for blueberry fortified synbiotic fruit yoghurt preparation. 10 kDa peptidefractionsfrom the fruit yoghurt showed the highest antioxidant activity (2076.02 µmol/liters TEAC) which was retained up to 20th days of storage (1925.84 µmol/liters TEAC) at refrigeration temperature. The antimicrobial activity (expressed in the zone of inhibition which ranged from 15.53±0.12 to 25.10±0.35 mm).
LC-MS/MS-MS sequencing of 10 kDa bioactive peptide fractions from yoghurt showed many peptide sequences like antioxidant peptides VPYPQ, AVPYPQR, KVLPVPE, VLPVPQKKVLPVPQK, GVRGPFPII, GPVRGPFPII, IPIQY, IPIQYVL, KVLPVPQ, VKEAMAPK and GVSKVKEAMAPK. ACE-Inhibitory peptides, antimicrobial peptides, immuno-modulatory peptides, anti-cancerous peptides and anti-thrombotic peptides were also identified.

Biofunctional Yoghurt
Soymilk supplemented with curcumin (@ 0.04%) and fermented with. L. acidophilus NCDC195 (LA195) and S. thermophilus NCDC323 (YC323) exhibited antimicrobial activity against a broad spectrum of pathogens and antioxidant activity (989.70 TEAC (μM)).

Curcumin Soy whey drink
LR28 showed maximum folate production (23.03±2.0 µg/l)at 2% inoculum level at 100 rpm in 48 h.Lactobacillus reuteri LR28 produced enhanced concentration of folate (35.12±0.92 µg/L) by the addition of 3% lactose, 5.5mg/l PABA and 300ul melon juices in skim milk. Lactobacillus reuteri LR28 showed significant improvement in diarrhea control in vivo.
LAB can be an effective method for preventing or treating hyperuricemia as some of the LAB has purine nucleosides degrading ability. Eleven isolates were positive for purine nucleoside degradation ability.
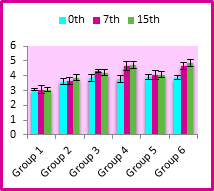
Intestinal Fluid Antibodies (IgA) by ELISA
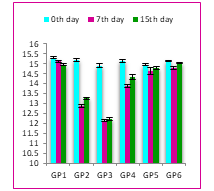
Haemoglobin in Animals
Biopreservation
Antimicrobial active film was prepared by coating the antimicrobial peptides and AFS produced by lactobacillus cultures (C25+195) in combination. The shelf life of market khoa was enhanced by 5 days inan active glassine paper and Al-foil. The shelf life of NDRI khoa sample wrapped in active Aluminium foil was enhanced by 10 days and in glassine paper by 5 days.
Antimicrobial film
Bacteriocin like substance of 4-5 kDa peptide was produced by Lactococcus lactis sp. lactis C63. Maximum bacteriocin activity was in MRS broth after 22 h incubation at pH 6.5 and 7.Micro-encapsulation of bacteriocins was done for its controlled release for preservation of Khoa and paneer.
Whey Utilization
The deletion of the two regulatory genes was employed in K. marxianus using the Cre-LoxP system for the efficient utilization of both glucose and galactose by preventing the catabolite repression. The engineered strain in concentrated whey yielded 47 g/L of ethanol during fermentation of concentrated whey containing 100 g/L of lactose which is 19% higher than the parental strain.
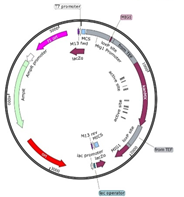
Deletion cassette of 2242 bp
Kluyveromyces marxianus MTCC 1389 tolerates sugar (lactose) up to 200 g/L, ethanol up to 6% and thermotolerant up to 45oC. Fermentation with adapted K. marxianus MTCC 1389 strain in 3L bioreactor resulted in final ethanol titer of 79.33 ± 0.82 g/L which was nearly 17.5% more than parental strain 65.66±0.12 g/L. Adapted strain was found stable even after 10 cycles of fermentation in whey (50g/L).
Trehalose contents from Kluyveromyces marxianusMTCC 1389 were found to be higher in osmotic stress i.e. 190 mg/g cell dry wt. and 121 mg/g cell dry wt. under NaCl (0.25M) and lactose (15% w/v) stress, respectively as compared to oxidative stress (100 mg/g cell dry wt.). Viability was also found to be higher at 0.25M NaCl and (15% w/v) lactose. The results of the study suggested that the trehalose plays a protective role primarily in osmotic stress.
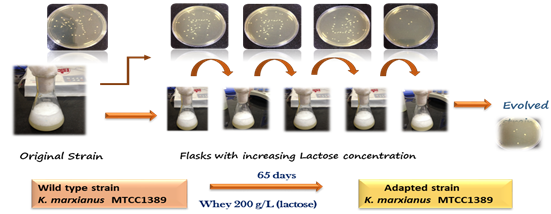
Evolution of K. marxianus 1389 cultures with concentrated whey 200 g/L
The biocatalyst β-galactosidase produced by lactose fermenting yeast 6C17 and 6C18 was immobilized on chitosan macroparticles using glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent with maximum immobilization yield of 97.4%.The immobilized enzyme retained 89% catalytic activity after 15 cycles of reuse. β-galactosidase was immobilized on chitosan and S. cerevisiae on calcium alginate for efficient use.
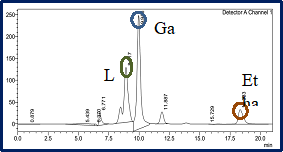
Lactose hydrolysis and ethanol production by immobilized S.cerevisiae along with chitosan immobilized β-galactosidase
Synbiotic Functional Foods and Bioremediation
- Process for blueberry fortified probiotic Dahi has been developed. The efficacy has been evaluated for prevention of colon cancer in rat model. The developed fermented product inhibits DMH induced colon carcinogenesis as compared to normal Dahi.
- Identified and evaluated efficacy of probiotic lactobacilli for prevention/treatment of non alcoholic fatty liver diseases in animal model. Feeding of probiotic fermented milk and cultures prevent non alcoholic fatty liver in mice w.r.t. genetic and biochemical markers.
- Identified novel strain of probiotic lactobacilli for biotransformation of cholesterol to coprostanol which reduce its deposition in body thus improve cardiovascular health in animal model.
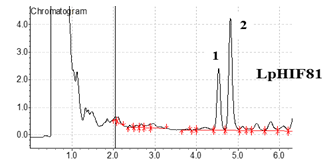

Gas chromatograms of cholesterol to coprostanol bio-converters L. plantarum HIF 81
- Characterized probiotic strains of lactobacilli to mitigate aflatoxins M1 menace.
- Biofilm forming bacteria have been isolated and characterized from dairy niche to develop strategies for biofilm control in dairy process lines.
- Sulphate reducing anaerobes have been identified to mitigate methane emission.
- Gene sequence of probiotic (6) and sulphate sequestering anaerobic bacteria (20) have been submitted to databank NCBI.
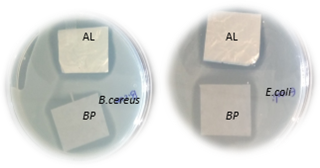
- Identified natural bio-molecules for their bio-preservative potential against food borne spoilage and pathogens including E. coli O157: H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in indigenous fermented (sweetened Lassi) and non fermented dairy (Paneer) products.
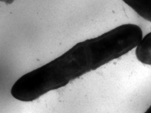
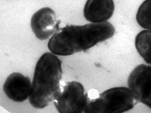
Transmission electron micrographs of L. monocytogenes ATCC 15313 (A) Untreated (B) trans-cinnamaldehyde treated
Microbial Biosensor, Food Safety and Quality Assurance Laboratory, National Referral Centre
Development of biosensor based diagnostics in the field of Food Safety and Quality Assurance at National Referral center on milk quality and safety (BSL-3), Dairy Microbiology division
Dairy Microbiology Division took a lead in establishing National Referral Center on Milk Quality and Safety (NRCMQS) with funding under World bank funded NAIP project with fund support of 17.5 Crores in 2014 for addressing the scientific issues on milk safety in our country with the mandate to provide scientific solution in specialized field of milk safety and quality assurance; to carry out Risk Profile Work on Potential Contaminants in milk and milk products; development of milk safety standards, sampling plan and testing procedures for regulatory compliance; Rapid Biosensor Based Tools/Assay/Kits for field application and to conduct training on HRD development on milk quality. State of the art laboratory having BSL-3 facility along with other equipment’s such as Biosafety cabinets, VIDAS multiple pathogen detection system, RT- PCR, Multimode plate reader, Centrifuge, Automatic media preparatory cum sterilizer, Biacore Surface Plasmon Resonance system, D count flow cytometer etc.
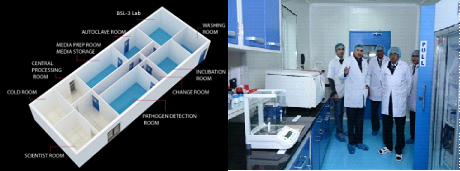
BSL -3 Containment Established at NRC
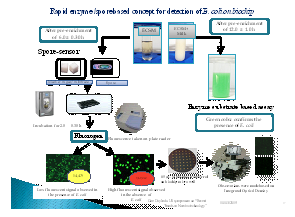
With the established facility at NRC, rapid sensors were developed for detection of potential contaminants in dairy food chain by exploring bacterial spores as biosensor. A large number of biosensor platforms have been developed for rapid on-site, real-time detection of various contaminants in food chains, however, their realization in commercial application is very low primary because of huge cost of either bio-recognition element or transducer involved in the development of biosensor. Bacterial Spore as innovative approach for its application as bio-recognition element was successfully employed in rapid detection of antibiotic, pesticides and bacterial contaminants in dairy foods and their commercialization under field condition.
Spores are dormant structures produced by a process of sporulation in a few species of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Bacillus and Clostridium. They are meant to survive unfavorable environmental conditions. Using spore-based biosensors for detection of varying range contaminants offers many advantages over existing methods. These developed biosensors are highly sensitive, reliable, user-friendly, cost-effective and with long shelf life. These contaminants may include different groups of antibiotics, pesticides, heavy metals, pathogenic microorganisms and several others that may be important for public health. Spore-based sensing technologies were developed to target many emerging contaminants in different types of food matrices, including milk and milk products in order to ensure food safety and quality.
Different types of approaches were attempted for the development of spore-based biosensors for detection of antibiotic, pesticides and bacterial contaminants in milk. A proof of concept for the detection of β lactam group of antibiotics in milk which works on the induction of β-lactamase enzyme in germinating bacillus spores. The concept was transformed on Paper strip for specific detection of β-lactam group of antibiotics as specified in CODEX/FSSAI standards in milk. The concept was transformed it into Microfluidic device in collaboration with University of Southampton, UK.
Fabrication of Paper based pillar array device: A paper-based pillar array device for the detection of ß-lactam group of antibiotics in milk was fabricated at the University of Southampton. The device was designed using AutoCAD and 2 mm (diameter) pillars were micro milled on a PMMA surface (1 mm height). The dimensions of the chip were 14 x 14 x 3 mm (width x length x height). Filter paper (whatman Grade 3) was cut into 2mm (diameter) and fixed on the pillar via a double sided tape. The substrate was then pipetted onto the paper (2 µL) and dried in an open air for 5 min. The step by step fabrication of the device is shown in Figure below.
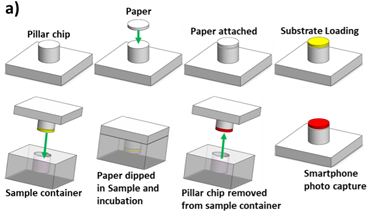
Schematic of the paper-based device for detection of Beta-lactam antibiotics in milk
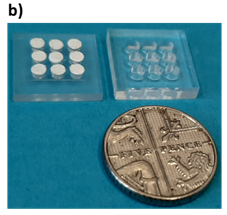
Photograph of the paper-based device (UK 5 pence coin)
Evaluation of fabricated device with pure β lactamase enzyme and its substrate: A paper-based pillar array device for detection of ß-lactam group of antibiotics in milk was fabricated at the University of Southampton during the visit. After fabrication of device, the working of the device has been tested with pH indicator and ß-lactamase with its substrate for the proof of concept. The device was found suitable for the reactions and proves the concept by using this device for multiple sample analysis in a single trial.
Paper-based pillar array devices




Validation of Paper based pillar array device with spore based paper strip: Milk samples were spiked with amoxicillin antibiotic and mixed with spores and nutrients to induce ß-lactamase production in germinating spores. Samples were loaded onto the container consisting of 2.4 mm wide and 2.4 mm deep wells and incubated at 37° C for 30 min, pillar chip was dipped into the samples (30 min incubation with substrate) and photos were taken as shown in Figure below. The detection of antibiotic was also tested by paper strips developed at NDRI, India and a great agreement was found between these two methods.

Photo showing incubation of nitrocefin (1mg/mL) coated paper with different concentrations of amoxicillin (1- 0 ppb; 2 – control milk; 3- 1 ppb; 4- 2 ppb; 5- 3 ppb; 6- 4 ppb; 7- 5ppb; 8 and 9- 10 ppb)
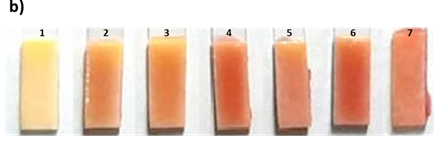
Representative examples of the same samples
These preliminary results indicate that further development of the paper-based device would lead towards the development of the quantitative tool for antibiotic detection in milk samples and hence, combating microbial drug resistance. This simple to fabricate and easy to operate inexpensive device along with smartphone detection has the potential to revolutionize the point-of care diagnostics industry for animal healthcare and antimicrobial resistance prevention in humans.
Paper Strip Based concept for Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk: Paper-based sensors are new alternative technologies for fabricating simple, low-cost, portable and disposable analytical devices for many application. The major advantages of using paper as a sensing platform include ease of availability, low cost, passive liquid transport, compatibility with chemicals/bio-chemicals and fast response. With these basic properties in mind, spore-germination inhibition based assay for antibiotic detection was developed on paper strip for exploring its potential under field application. The stages involved in developing paper sensors includes the proper choice of paper, fabrication/patterning and semi- quantitative analysis based on color development as a result of specific marker enzymes released during spore germination .The test involves pre-dipping of strip in milk and germination of spores in presence of germinant mixture when incubated at 64o C for 1:15 hrs. Development of blue color on paper strip indicates absence of antibiotic residues and no color development indicates presence of antibiotic Residues in milk.
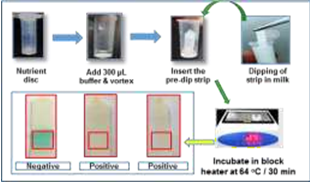
Paper Strip Based concept for Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk
Paper strip based assay for antibiotics detection in milk, was validated by third party through an open tender and M/s. Dove Research and Analytics, Panchkula(A unit of Dove Chemicals) validated the claims of the technologies, in terms of working test procedure, sensitivity against various groups of antibiotics as per Limits of Detection (LODs). Certificate no DRA/NDRI/16-17/080217 /002 dated9-2-2017. Patent of the technology has been published (2213/DEL/2014) in IPO Journal no. 07/2016, U/S 11A dated 2016/02/12. Technology MOU was signed on Technology entitled Paper strip for detection of antibiotic residues in milk under outreach project funded by ICAR. M/s. Florecer Services Private Limited, New Delhi, adopted technology through agri inovate with non-exclusive license fee of Rs.5.90 Lakhs+ 2% Royalty dated 01 July 2019.
Spore Based Kit for Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk at Dairy Farm: The developed technology is working on principle of spore germination and its inhibition in presence of antibiotic residues in milk. In case when antibiotic residues are absent in milk, marker metabolites are released during germination which change the color of the indicator. However, in presence of antibiotic residues in milk, the spore germination process is inhibited at ≥ MRL level of contaminants and no change in color indicates the presence of drug residues in milk when incubated at 64oC for 2.30 hrs.

Kit for Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Milk at Dairy Farm
Spore based kit for detection of antibiotic residues in milk at dairy farm was validated by third party through an open tender and M/s. Dove Research and Analytics, Panchkula (A unit of Dove Chemicals) validated the claims of the technologies, in terms of working test procedure, sensitivity against various groups of antibiotics as per Limits of Detection (LODs). Certificate no DRA/NDRI/16-17/080217/001dated9-02-2017. Patent on this technology was granted (No: 264145) dated 9.12.2014.the technology was commercialized to M/s. Neugen Diagnostics India Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad with license fee of 2.5 lakhs on 17th Dec 2008; M/s. Hatsun Agro Product limited, Chennai on 17th Dec 2016. With license fee of 3.0 lakhs and M/s. Delmos Research Pvt. Ltd. 5210 / 29, Surat Nagar Phase 1, Gurgaon 122001 adopted technology through Agri inovate pvt ltd , New Delhi and MOU signed dated 12 March 2019 with an revenue of Cost of technology: Rs. 3.0 Lakhs + 18% GST) Rs. 3.54 Lakhs.
Paper Strip based concept for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues: Pesticides are well known carcinogen and their impact on human beings and presence in different food products including milk are well known in the prior art. The existing conventional chromatographic methods (LC/GC-MS) are time- consuming and laborious. Currently, new standards for pesticides have been developed by FSSAI and implemented for regulatory compliance in different food products including milk. For routine monitoring of pesticides under field application, three stage assay on paper strip has been developed based on “spore germination and enzyme inhibition principle”. In case where analyte i.e. pesticide is absent, specific marker enzyme (s) are produced by spores during germination which will act specifically on chromogenic substrate resulting in colored end product on paper strip, whereas complete inhibition of marker enzyme will take place when pesticides are present in food sample (Patent Reg. 3819/DEL/2015).Simple and cost- effective technology for field application for testing of pesticides residues in milk, cereal based foods, fruit juices, feed, fodder, soil, water, manure etc.

Paper Strip based concept for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues
Third party validation of developed sensor work on paper strip based assay was carried out at NABL accredited SGS laboratory, Gurgaon by spiking different pesticide groups in reference reconstituted milk (pesticide free milk) in duplicate at 3 different concentrations. The results obtained with developed assay which includes extraction of pesticides from milk and its detection by paper strip based assay and comparative analysis with GC-MS/MS, LC-MS indicated similar results by both the methods. The limit of detection (LODs) as claimed were found reproducible during validation work. No false positive or negative results were observed. Certificate no ref no gg17-001563.001 dated 20-4-2017.The patent of the technology has been published in Indian Patent journal (No. 3819/ DEL/ 2015) no 21/2017 dated 26 May 2017. Technology was commercialized to M/s. Hatsun Agro Product Limited, Chennai adopted the technology through MOU Dated 17th Dec, 2016, exchanged during NDRI industry meet dated 17th Dec 2016 witha non-exclusive license with an amount of Rs. 5, 75,000.00 and subsequently transferred to M/s. Florecer Services Private Limited, New Delhi, adopted technology through agri inovate with non-exclusive license fee of Rs.5.90 Lakhs+ 2% Royalty dated 01 July 2019.
A miniaturized spore based assay for detection of bacterial contaminants in milk on functionalized gold chip with minimal quantity of milk and other reagents with enhanced sensitivity was developed. The developed assay was integration with other consortia partners to have multi-analyte high throughout put analysis for dairy applications. The spore enzyme assay was evaluated on biochip using EMCCD camera. The fluorescent signals were quantified in terms of integrated optical density (IOD).Patent on the technology has been published in IPO (1357/ DEL /2013) in Indian patent journal no. 50/2014, Dated12/12/2014
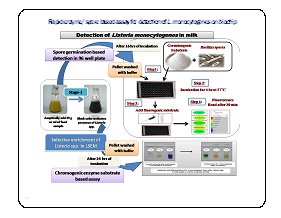
Third Party Validation: SGS Referral Laboratory, M/s SGS India Pvt. Ltd., Gurgaon, validated Technology was validated by conducting different trials for false positive/false negative results and the working performance of two stage enzyme based for detection of L. monocytogenes within real time of26±0.15+4=30.30±0.15hrs.wascomparedwith ISO 11290 Part-1 1996 method (7-days protocol) and results were found in accordance with the claimsofthedevelopedenzymebasedassayVide Ref No Job No Gg 12-009772.001Dated 9/11/2012. Technology on Listeria monocytogenes and Enterococci were licensed to M/s. Neugen Diagnostics India Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad with revenuegenerationof7.5lakhsand 3.5 lakhs dated 5thJuly, 2013 respectively.
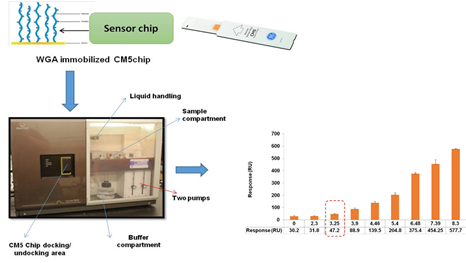
Surface Plasmon Resonance based detection of Listeria monocytogenes
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) method for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes was optimized using Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) lectin with a detection sensitivity of 3.0 log cfu/ 100µl in buffer and milk system, respectively. Developed SPR has shown minimum false positive and negative reaction with other G+Ve and G-ve bacteria with the detection time of around 20-30 min, respectively.
Surface Plasmon Resonance based detection of Listeria monocytogenes using Wheat Germ agglutinin
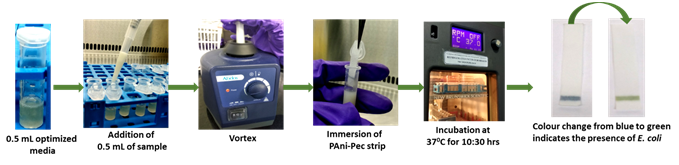
- Protocol for synthesis of Polyaniline-pectin conducting polymer particles was optimized and the particles were characterized using FT-IR and particle size analyser using Zeta-size analyser. A paper strip based assay has been developed using PANI-PEC particles immobilized paper strips for the detection of E. coli and coliform in milk using newly developed ECS medium and CSM, respectively with the a detection limit of 0.5 log cfu/100 µl within a time period of 10 ½ hrs. A paper strip based assay has been developed using PANI-PEC particles immobilized paper strips for the detection of total microbial load in milkin milk using newly optimized medium with a detection sensitivity in the range of 0.5 to 8.5 log cfu/ 100ul and with a detection of time of 5-6 hrs using newly optimized broth medium.
- Surveillance of antibiotic resistant E. coli in milk supply chain was undertaken in our lab and E. coli isolates have shown resistance towards cefepime, gentamicin, erythromycin, trimethoprim, chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline and 4 among these isolates have shown resistance to ESBL antibiotics (harboring the CTX-M gene).
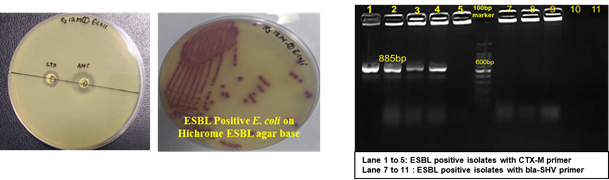
Prevalence of ESBL positive E. coli in milk
- Protocol for the synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on iron magnetite encapsulated polymer of methacrylate (monomer) and ethylene-glycol-di-methacrylate (monomer-cross-linker) for selective extraction of captan pesticide from natural sample. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer mediated enzyme inhibition based microtiter assay for the detection of Captan pesticide has been developed with a LOD of 0.1 ppb and 88.61±0.22% recovery of captan pesticide in water samples.
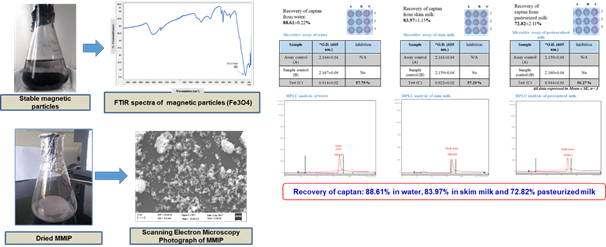
Determination of recovery of captan from water, skim milk and pasteurized milk by HPLC using MMIP
- Back to previous page
- |
-
Page last updated date:19-02-2025 04:01 PM